A Hot Swap is basically the exchange of PC periphery while the system is running. The components that need to be exchanged, are not connected to the operating system or any other software. In doing so, neither the power supply is interrupted, nor the system is rebooted.
Let’s assume that a fan shows damage while the PC is running: Thanks to Hot Swapping the broken fan can be exchanged easily. But also other components, such as SSDs that are connected via RAID, can be hot swapped. In another article we already explained what a RAID level is.
Basis for Hot Swapping
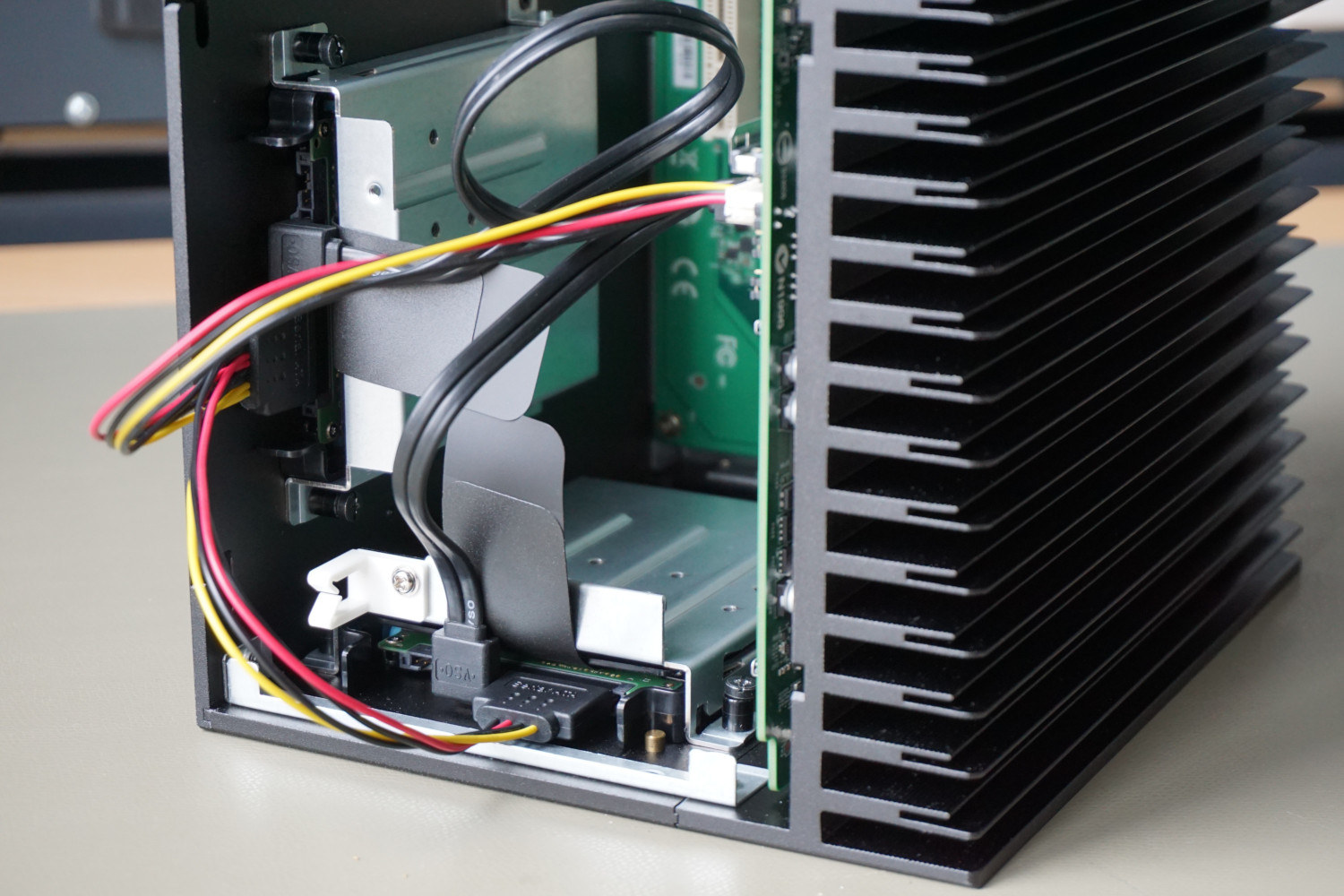
A plug connection has to tick some boxes, so that the component can be hot swapped. It is required that the plug has leading contacts, that means the contacts are connected and disconnected in a well-defined order, mostly in three or more steps. This is realized by a common housing, in which the contacts are shifted forward or backwards. The most established systems with leading contacts are SATA and USB (see image 1).
The user should furthermore plug the connector in and out linearly and slowly.
Which advantages does Hot Swapping have?
As mentioned previously, the benefit of Hot Swapping is that it is not necessary to reboot or interrupt the system to replace faulty components. Especially for servers and in the industrial sector, where PCs must run 24/7, the fast exchange of components via Hot Swap has a crucial advantage, because even the shortest interruption can mean an enormous loss.
Modifications of Hot Swapping
- Hot Add: Stands for adding new components, that work in the running system without configuration.
- Hot Plug: Stands for adding and removing components during the running system, if no software is involved, also known as Plug and Play.
- Hot Switch: Stands for switching between components, for instance to a redundant concurrent power supply unit.